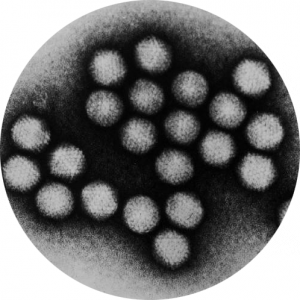
VIRUS: SARS-CoV-2 (CORONAVIRUS)
The complete clinical picture of COVID-19 is not fully known.
An epidemic of viral pneumonia of unknown etiology emerged in the city of Wuhan, China in December 2019. On January 9, 2020, the discovery of a new coronavirus was officially announced by WHO. This new virus is the agent responsible for this new infectious respiratory disease called Covid-19 (CoronaVIrus Disease).
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are common in people and many different species of animals, including camels, cattle, cats, and bats. Rarely, animal coronaviruses can infect people and then spread between people such as with MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and now with this new virus, named SARS-CoV-2. However, the source of the transmission has not yet been identified with certainty.
Reported illnesses have ranged from very mild to severe, including illness resulting in death. People with serious underlying medical conditions ( heart conditions, chronic lung disease, and diabetes, for example) also seem to be at higher risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness.
ATA RESULTS:
New coronavirus (COVID-19) is part of the Coronaviridae family, made up of a lipid membrane of cellular origin. We tested our F7 + H14 filtration chain and photocatalysis decontamination technologies, and Bioxygen® module on the H1N1 Influenza virus, from the lipid membrane category, like that of coronaviridae, we obtained 99.9929{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} retention in a confined space of 2.5 m3 in 5 minutes.
GRAM POSITIVE BACTERIA TYPES: BACILLUS SUBTILIS SPORES
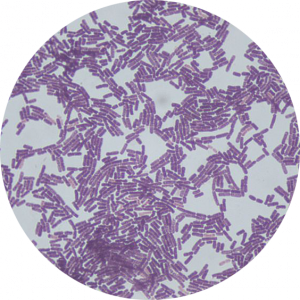
Bacillus subtilis, also known as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium.
Bacillus subtilis is is readily present everywhere; the air, soil and in plant compost.
Bacillus subtilis bacteria are non-pathogenic. It spends most of it time inactive and in spore form, and when the bacterium is active, it produces many enzymes, that can result in food contamination.
According to a study made by the University of Connecticut Health Center, spores produced by the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis are much more resistant to wet heat than are their growing cell counterparts.
Its conclusion points out the importance in the choice of conditions for preparation of surrogate spores for use in monitoring the efficacy of sterilization conditions, as the precise temperature used can have an enormous effect on the resistance of the resultant spores to some treatments
Bacillus subtilis bacteria are non-pathogenic. It spends most of it time inactive and in spore form, and when the bacterium is active, it produces many enzymes, that can result in food contamination.
ATA RESULTS:
A recent study conducted by VirNext shows that systems developed by ATA allows the decontamination of a confined space of a volume of 2.5m3 in 5 minutes with efficiencies of 95.234{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} for Bacillus subtilis spores. This study proves also that ATA system can decontaminate air of confined space containing same type of bacteria spores, such as bacillus anthracis, bacillus cereus…
GRAM POSITIVE BACTERIA TYPES: PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA
Pseudomonas genus is a group of more than 140 bacterial species, all strictly aerobic Gram-negative rods, widely found in the environment, including in and around water sources.
The most common species in the context of human health is Pseudomonas aeruginosa, where estimates of colonization vary from 3–5{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} in healthy individuals up to 20{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} among inpatients – especially with compromised host defense mechanisms.
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa is a common Gram negative bacteria, that causes important infection, especially in patients with compromised host defense mechanisms. It is the most common pathogen isolated from patients who have been hospitalized longer than 1 week, and it is a frequent cause of nosocomial infections. Pseudomonial infection can involve the followings diseases:
– Pneumonia
– Meningitis, brain abscess
– Bacteremia
– Urinary tract
– Osteomyelitis
– Bacterial keratitis, endophthalmitis
– Endocarditis
– Otitis externa and media
– Enterocolitis, diarrhea..
– Ecthyma gangrenosum
Treatment of patients with P. aeruginosa is complex as a result of inherent resistance to many antimicrobials and, increasingly, acquired resistance to the remainder.
According to a study led by the Wythenshawe Hospital in Manchester, the isolation of epidemic strains of P aeruginosa from room air suggests that aerosol dissemination may be the most important factor in patient-to-patient spread during the recent cross infection outbreak.
– Meningitis, brain abscess
– Bacteremia
– Urinary tract
– Osteomyelitis
– Bacterial keratitis, endophthalmitis
– Endocarditis
– Otitis externa and media
– Enterocolitis, diarrhea..
– Ecthyma gangrenosum
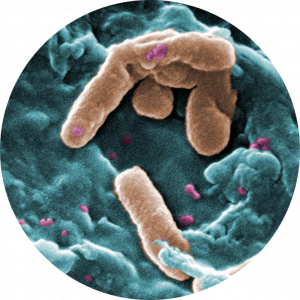
ATA RESULTS:
To avoid such issue with Gram negative bacteria, the system developed by ATA-Medical Company allows the decontamination of a confined space of a volume of 2.5m3 in 5 minutes with efficiencies of 99.965{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These results are also efficient on other Gram negative bacteria such as Bordetella pertussis, or Diplococcus bacteria..
GRAM POSITIVE BACTERIA TYPES: ESCHERICHIA COLI
ATA RESULTS:
Like with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, ATA devices allow the decontamination of a confined space of a volume of 2.5m3 in 5 minutes with efficiencies of 99.925{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} Escherichia coli, a gram negative bacteria.
Escherichia Coli is a gram-negative commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. There are hundreds of strains of the bacterium, but E. coli has been identified as dangerous to people, producing a powerful toxin that can cause severe illness. Once someone has eaten contaminated food, the infection can be passed from one person to another person by hand-to-mouth contact.
The Bacteria are most often spread person to person.
Escherichia coli may cause many common bacterial infections, including cholecystitis, bacteremia, cholangitis, urinary tract infection (UTI), and traveler’s diarrhea, and other clinical infections such as neonatal meningitis and pneumonia.
GRAM POSITIVE BACTERIA TYPES: STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
Due to the over-use of antibiotics, strains of bacteria become more resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics, and lead into the increase of bacteria such as the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). MRSA can survive on surfaces or skin scales for up to 80 days.
These bacteria are spread by direct contact with an infected person, by using a contaminated object, or by inhaling infected droplets dispersed by sneezing or coughing.
Airborne transmission is generally considered to occur at lower frequency than transmission via direct contact, but MRSA in the form of a bioaerosol can contaminate air and cause airborne infection. According to a study published from the The Hospital Infection Society, MRSA was mainly carried on larger particles, 4-8 mm in size but some were on <4µm particles, so were respirable; able to reach the lung and possibly cause infection.
Staphylococcus aureus infections range from mild to life threatening:
– Skin infection causing abscesses or bacteremia by traveling through the bloodstream.
– Heart valves infection (endocarditis) or bones (osteomyelitis).
– Lung infection (pneumonia)
– Heart valves infection (endocarditis) or bones (osteomyelitis).
– Lung infection (pneumonia)
ATA RESULTS:
According to a recent study conducted by a Virnext laboratory, ATA products allows the decontamination of a confined space of a volume of 2.5m3 in 5 minutes with efficiencies of 99.842{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} for Staphylococcus aureus. These results are also efficient on any other airborne Gram positive bacteria, such as Corynebacterium diphtheria; or Streptococcus pneumoniae.
GRAM POSITIVE BACTERIA TYPES: ENTEROCOCCUS FAECIUM
ATA RESULTS:
According to a recent study conducted by a certified laboratory, ATA products allows the decontamination of a confined space of a volume of 2.5m3 in 5 minutes with efficiencies of 99.800{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} for Enterococcus faecium. These results are also efficient on any other airborne Gram positive bacteria, such as Corynebacterium diphtheria; or Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Enterococcus Faecium is a Gram-positive bacteria : it can be commensal in the human intestine, but it may also be pathogenic, causing diseases.
The genus Enterococcus includes more than 17 species, although only a few cause clinical infections in humans genre.
Since the beginning of the antibiotic era, they have posed major therapeutic challenges, as they acquire resistance to many antimicrobials, resulting in multidrug-resistant strains with limited treatment options. The two main pathogenic enterococcal spp are E faecium and E faecalis.
According to J. Scott Weese, DVM, DVSc, DACVIM University of Guelph, Enterococci are transmitted by direct and indirect contact, not airborne or aerosol routes, so proper use of standard practices should minimize risk of transmission.
MOULD: CANDIDA ALBICANS
Candida albicans is a dimorphic fungus that grows both as yeast and filamentous cell.
Candida yeasts normally reside in the intestinal tract and can be found on mucous membranes and skin without causing infection; but when the environment is right, the yeast can multiply and grow rapidly.
With airborne transmission, candida yeast spreads in the mouth and throat and cause thrush to patient due to the Oropharyngeal Candidiasis.
ATA RESULTS:
This type of mould can be eradicated at a level of 99.973{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} in a confined space of a volume of 2.5m3 in 5 minutes with the solutions developed by ATA. This test has been conducted by a certified laboratory which proved that the ATA filter system units allows to decontaminate air of confined space containing mould and yeast.
MOULD: ASPERGILLUS FUMIGATUS
ATA RESULTS :
To fight against this growing problem in hospitals, ATA developed solutions able to eradicate 99.467{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} of Aspergillus fumigatus in a confined space of a volume of 2.5m3 in 5 minutes. Test, which has been driven by a certified laboratory, proves the efficiency of the ATA filter systems also on mould and yeast.
With the continuing increase in the number of severely immunocompromised patients, hospitals are faced with the growing problem of invasive aspergillosis.
A recent study led by Department of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Mara, revealed that abnormally high levels of airborne A. fumigatus conidia correlated with new cases of IA, even in patients who were not severely immunocompromised.
While for healthy individuals the innate immune system is an efficacious barrier to Aspergillus fumigatus infection, it is the most frequent cause of invasive fungal infection for immunosuppressed individuals. When Aspergillus spores infect the lungs and then migrate into the bloodstream, traveling to other organs and spreading the infection; it causes the life-threatening fungal infection called Invasive Aspergillosis.
While for healthy individuals the innate immune system is an efficacious barrier to Aspergillus fumigatus infection, it is the most frequent cause of invasive fungal infection for immunosuppressed individuals. When Aspergillus spores infect the lungs and then migrate into the bloodstream, traveling to other organs and spreading the infection; it causes the life-threatening fungal infection called Invasive Aspergillosis.
VIRUS: INFLUENZA H1N1
Influenza occurs all over the world, with an annual global attack rate estimated at 5–10{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} in adults and 20–30{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} in children. These results are explained by its high mutation rates and easy transmission from person to person.
Influenza is spread by coughing and sneezing, which release the germs into the air and can be breathed in by others.
According to Bischoff from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, hospitalized patients can generate influenza-containing aerosols up to 6 feet with concentrations higher than the infectious dose, but these findings require confirmation before widespread changes in infection control strategies are implemented.
Complications of influenza viral infection include: primary influenza viral pneumonitis, bacterial pneumonia, otitis media and exacerbation of underlying chronic conditions. Illness tends to be most severe in the elderly, in infants and young children, and in immunocompromised hosts.
ATA RESULTS:
To prevent such results, the system developed by ATA allows the decontamination of a confined space of a volume of 2.5m3 in 5 minutes with efficiencies of 99.9929{01e3c5e93231d16e008ef94f2b1d6fd0127ff363a7cc717001d1444d838f865e} for Influenza H1N1 and is efficient on any mutation form of the H1N1.
VIRUS: ADENOVIRUS TYPE 5